
Copper Parts and Components for Electrical, Thermal and Industrial Applications
Copper parts and components are used across electrical, electronics, HVAC, plumbing, automotive and construction sectors because of copper’s outstanding electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance and formability. These properties make copper a core material for both high‑performance functional parts and premium architectural elements.
Exceptional Electrical Conductivity
Copper’s electrical conductivity is among the highest of all engineering metals, which makes copper components indispensable in power and signal applications. Typical uses include:
- Power cables, busbars and distribution components
- Connectors, terminals and contact parts
- PCB and electronic interconnect hardware
High conductivity minimizes energy loss, improves efficiency and supports stable operation in everything from low‑voltage electronics to high‑capacity power systems.
Thermal Management and Heat Dissipation
- Copper’s excellent thermal conductivity allows it to move heat away from critical areas quickly and efficiently. Common thermal applications include:
- Heat exchangers and condensers
- Radiators and cooling circuits in automotive and machinery
- Heat sinks and cooling plates in electronics and power electronics
- Effective thermal management using copper components helps increase performance, extend service life and improve reliability of equipment.
Corrosion Resistance and Long Service Life
Copper naturally resists many forms of corrosion, particularly in atmospheric and many aqueous environments. This makes copper parts suitable for:
- Plumbing and water distribution systems
- Marine and coastal installations
- Outdoor electrical and architectural components
Corrosion resistance helps copper components maintain structural and functional integrity over long periods, reducing maintenance and replacement frequency.
Malleability, Machinability and Design Flexibility
Copper is easy to form, machine and join, enabling complex and customized component designs. Manufacturers can:
- Produce intricate shapes via machining, stamping, forging or casting
- Achieve fine details and tight tolerances for precision parts
- Join components by soldering, brazing or welding for robust assemblies
This flexibility supports both standard parts and highly tailored solutions for specialized applications.
Versatile Applications Across Industries
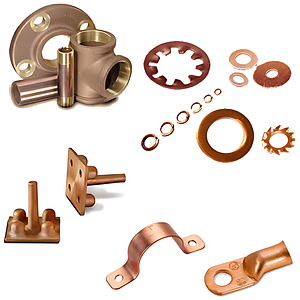
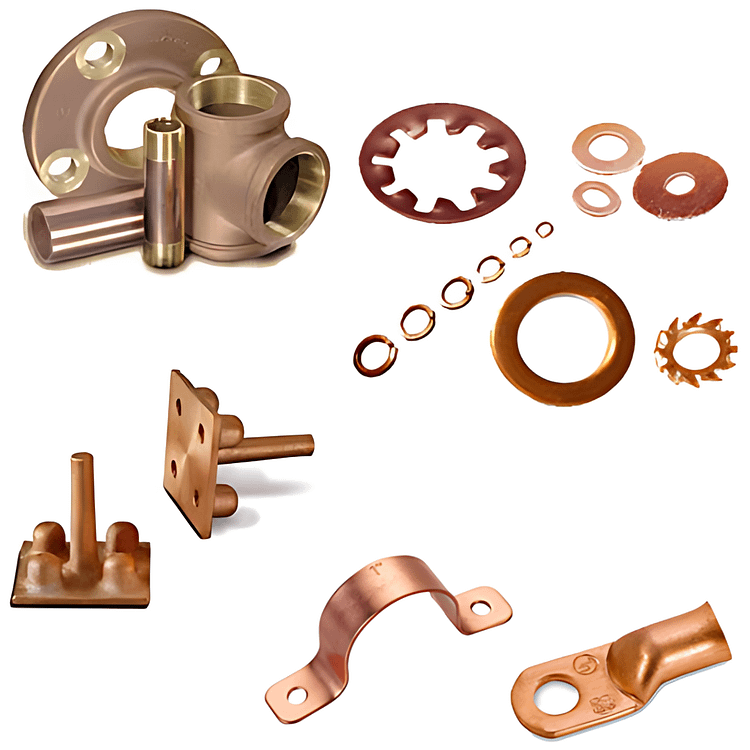
Thanks to its balanced properties, copper is used in a wide variety of components, such as:
- Electrical connectors, lugs, busbars and contact elements
- Plumbing fittings, manifolds and water distribution components
- HVAC coils, headers and fittings
- Automotive and rail electrical and cooling parts
- Building façades, roofing elements and decorative trims
This breadth of use highlights copper’s role as a foundational engineering material.
Health, Hygiene and Safety
In plumbing and water systems, copper’s inherent antimicrobial behavior helps inhibit the growth of harmful microorganisms on internal surfaces. This supports:
- Safer, cleaner water in residential and commercial plumbing
- Improved hygiene in healthcare, hospitality and food‑service applications
These characteristics contribute to healthier environments and more reliable water quality.
Aesthetic Appeal in Architecture and Design
Copper’s distinctive reddish‑brown color and the natural patina it develops over time add strong visual value. Designers use copper components for:
- Roofing, cladding and façades
- Architectural details and ornamental work
- Interior accents, hardware and design features
The evolving patina can be either celebrated for a living, aged appearance or controlled through coatings and finishes depending on design intent.
Sustainability and Recyclability
Copper is fully recyclable and retains its performance characteristics after recycling. Using copper parts and components supports:
- Reduced demand for virgin raw material
- Lower environmental impact compared with many alternatives
- Circular‑economy approaches in manufacturing and construction
Long service life plus high recyclability make copper a sustainable choice for modern engineering and building projects.
Conclusion
Copper parts and components combine exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, formability and visual appeal, which makes them essential in sectors ranging from power and electronics to plumbing, HVAC, transportation and architecture. With strong sustainability credentials and broad design flexibility, copper continues to be a preferred material for high‑performance, durable and aesthetically refined solutions in global applications.