Copper Brass Earthing Clamps for Reliable Grounding Systems
Copper brass earthing clamps are pivotal in ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical systems. Used predominantly in grounding applications, these clamps provide a secure and reliable connection to the earth, which is essential for the safe operation of electrical circuits. Understanding their importance, applications, and benefits can provide insight into why these components are indispensable in both residential and industrial electrical setups.
Why Earthing is Essential
Effective earthing ensures that fault currents and overvoltages are safely diverted into the ground instead of through equipment or people.
- Reduces electric shock risks by providing a controlled path for fault current.
- Protects appliances and sensitive devices from surges and lightning strikes.
- Stabilizes system voltage by establishing a common reference point.
- Lowers the risk of electrical fires caused by overheating and arcing.
Because the earthing path is only as good as its weakest link, using robust, conductive earthing clamps is essential for overall system safety.
Material Advantages: Copper + Brass
Copper brass earthing clamps typically use high‑conductivity copper alloys and brass to balance electrical performance and durability.
- Copper delivers low resistance for efficient dissipation of fault and lightning currents.
- Brass offers excellent mechanical strength and resistance to corrosion and weathering.
- The combination provides long‑lasting electrical and mechanical performance in outdoor and industrial environments.
These properties make copper brass clamps suitable for long‑term installations where reliability is critical.
Key Applications of Copper Brass Earthing Clamps
Copper brass earthing clamps are used across residential, commercial, utility, and renewable energy installations.
- Residential and commercial buildings: Grounding main panels, distribution boards, and metal structures to protect occupants and equipment.
- Industrial plants: Earthing heavy machinery, process equipment, and structural steel for fault protection and EMC performance.
- Telecommunication towers and data centers: Lightning and surge protection for tower structures and critical IT infrastructure.
- Solar and wind installations: Grounding module frames, mounting structures, and equipment to safeguard renewable energy systems.
- Utilities and substations: Earthing poles, substation structures, fences, and grids to maintain grid stability and safety.
Their wide applicability reflects the importance of reliable grounding in every type of electrical network.
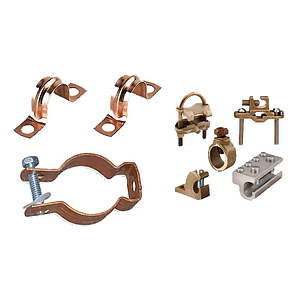
Common Types of Earthing Clamps
Different grounding layouts and conductors require different clamp designs.
- U‑bolt clamps: For connecting round conductors to earth rods or pipes, with adjustable and secure clamping.
- Parallel groove clamps: For joining two parallel conductors without cutting, often used in bonding and grid connections.
- Rod‑to‑tape clamps: For connecting earth rods to copper tape in building and lightning protection systems.
- Pipe clamps: For bonding earthing conductors to metal pipes, rails, or structural members.
- Split‑bolt clamps / junction clamps: For mechanically strong junctions between multiple conductors in earthing networks.
Selecting the right clamp type and size ensures a mechanically strong and electrically efficient bond.
Rod to Tape Clamps are designed to connect earthing rods to copper tapes, commonly used in earthing systems where tapes are used for grounding. Pipe Clamps are used to connect earthing conductors to metal pipes, ensuring a solid and stable grounding connection. Split Bolt Clamps are used for joining multiple conductors together securely, providing a robust connection point in grounding systems.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Correct installation is essential for earthing clamps to perform as designed.
- Choose clamp size and type based on conductor form (rod, tape, cable) and dimensions.
- Clean contact surfaces to remove dirt, paint, grease, or oxide layers before clamping.
- Tighten to the recommended torque to avoid loose connections or damage to conductors.
- Periodically inspect clamps for looseness, mechanical damage, or signs of corrosion, especially in harsh outdoor environments.
Regular inspection and tightening help maintain low resistance and system reliability over the life of the installation.
Securely tighten the clamps to ensure a firm connection, avoiding over-tightening as this can damage the conductors or the clamp itself. Periodically inspect the earthing clamps for signs of corrosion, wear, or loose connections. Regular maintenance ensures the longevity and reliability of the earthing system.
Benefits of Copper Brass Earthing Clamps
Using quality copper brass earthing clamps delivers several long‑term advantages.
- High conductivity: Supports low‑impedance fault paths and effective surge dissipation.
- Corrosion resistance: Withstands weather, moisture, and pollution, maintaining performance for many years.
- Mechanical strength: Tolerates vibration, thermal expansion, and mechanical stress without loosening.
- Versatility: Available in many sizes and designs for residential, commercial, industrial, and utility applications.
- Compliance: High‑quality clamps help meet grounding and lightning protection standards and inspection requirements.
- Cost‑effectiveness: Long service life and improved safety reduce downtime, damage, and maintenance costs.
These benefits make copper brass earthing clamps a sound investment in both safety and system reliability.
Conclusion
Copper brass earthing clamps play a critical role in grounding systems by providing durable, low‑resistance connections between conductors and earth electrodes. Their combination of conductivity, corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and design versatility makes them suitable for applications ranging from homes and factories to telecom towers, solar plants, and substations. By selecting and installing the right copper brass earthing clamps, electrical professionals can significantly enhance the safety, performance, and regulatory compliance of modern electrical installations.